
(ii) Dynamics: It relates the motion of objects to the forces which cause them. (i) Kinematics: It describes the motion of objects, without looking at the cause of the motion. There are two branches in physics that examine the motion of an object. The concept of motion is a re’ live one and a body that may be in motion relative to one reference system, may be at rest relative to another. “An object is said to be in motion if its position changes with time”. Even if you appear to be standing still, the Earth is moving around the sun, and the sun is moving around our galaxy. It might only be a small amount of movement and very-very slow, but movement does happen. Motion is one of the significant topics in physics. Motion in a Straight Line Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 3
#ACCELERATION FORMULA PHYSICS PDF#

In addition, such a graph appears also in the projectile motion problems.Īs said, the curve of the position-time graph is a parabola that has a quadratic form. $a<0$ as can be seen from the concavity downward of the curve) until reaches point B (figure below) where its velocity gets zero, changes its direction, and returns to the starting point in the opposite direction.Īs you guess, this is exactly a description of motion that appears in all freely falling problems. Solution: Physical interpretation of graph: This object starts its motion at some initial velocity (because the slope at time $t=0$ makes an angle with horizontal) and decreases its speed at a constant rate (i.e. Find the equation of the object's velocity as a function of time. time graph of a moving object along a straight line is a parabola as below. Suppose you are driving a car at a constant speed of $100\,$.Įxample (7): The position vs.

You can skip this introduction and refer to the worked examples.Īn object can move at a constant speed or have a changing velocity.
#ACCELERATION FORMULA PHYSICS HOW TO#
In this long article, we want to show you how to find constant acceleration from a position-time graph with some solved problems. A graph, looking like an upside-down bowl, represents a negative acceleration and vice versa. Or graphically, by observing the curvature of the $x-t$ graph. time graph can be obtained, numerically by having the initial position and velocity of a moving object
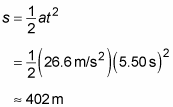

time graph?Īnswer: Acceleration on a position vs. How to find acceleration from a position vs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
